The Role of Blockchain in Facilitating Global Trade
- Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology
- Benefits of Using Blockchain in Global Trade
- Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Blockchain in Trade
- Real-world Examples of Blockchain Applications in International Trade
- Regulatory Frameworks and Standards for Blockchain in Global Trade
- Future Trends and Opportunities for Blockchain in Facilitating Trade
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that allows for secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. It operates on a network of computers, known as nodes, that work together to validate and record transactions in a chronological chain of blocks. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block, forming a secure and tamper-proof record of all transactions.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its immutability, meaning that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This makes blockchain an ideal solution for industries like global trade, where trust and transparency are essential. By using blockchain technology, parties involved in a trade transaction can have confidence that the information recorded on the blockchain is accurate and cannot be tampered with.
Another important aspect of blockchain technology is its ability to streamline and automate processes through smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud or errors in the transaction process.
In the context of global trade, blockchain technology can revolutionize the way international transactions are conducted. By providing a secure and transparent platform for recording and verifying trade transactions, blockchain can help reduce the time and costs associated with cross-border trade. Additionally, the use of smart contracts can help automate processes such as customs clearance, payment settlements, and supply chain management, further improving efficiency and reducing the risk of disputes.
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to transform the global trade industry by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient platform for conducting international transactions. By leveraging the benefits of blockchain technology, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and build trust with their trading partners, ultimately facilitating smoother and more reliable global trade.
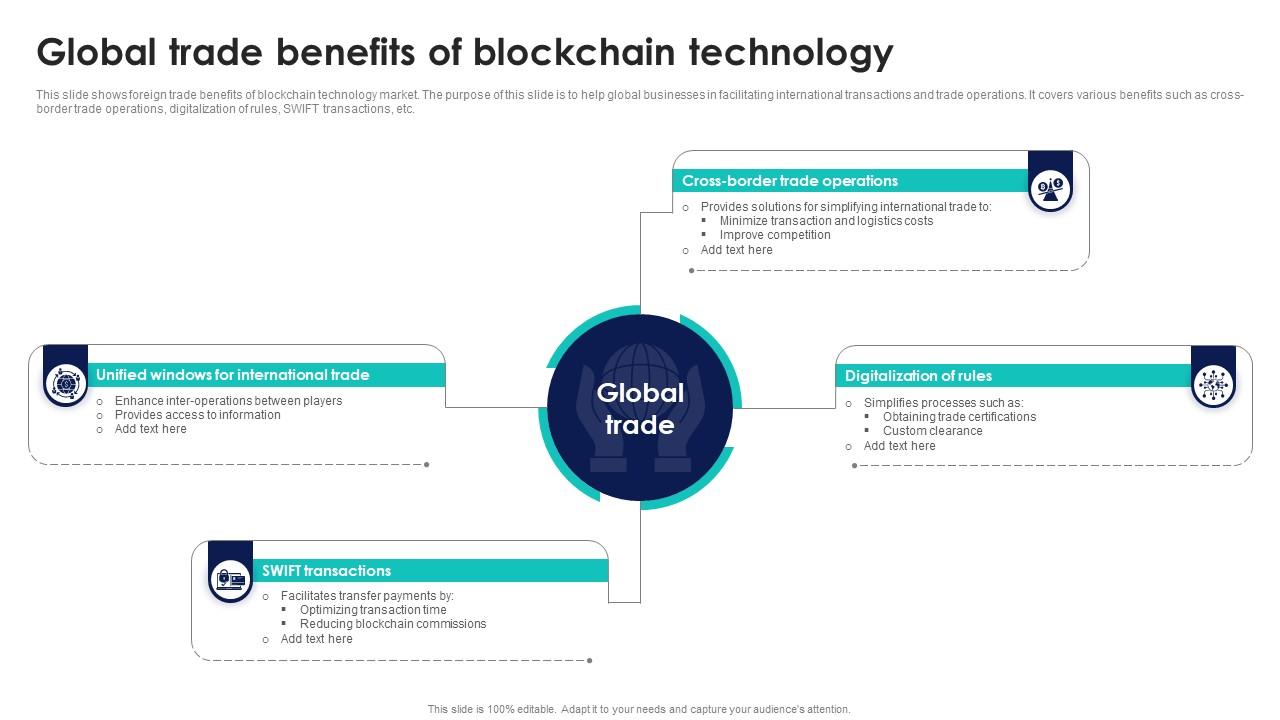
Benefits of Using Blockchain in Global Trade
Utilizing blockchain technology in global trade offers a myriad of benefits that can revolutionize the way businesses conduct transactions and manage supply chains. Some of the key advantages of using blockchain in global trade include:
- **Increased** transparency: Blockchain **provides** a decentralized and immutable ledger that **allows** all parties involved in a trade **to** access **real-time** information **about** the **transaction**. This **enhances** transparency **and** trust **among** participants.
- **Enhanced** security: **The** cryptographic **nature** of blockchain **ensures** that **data** **is** secure **and** tamper-proof. **This** **reduces** the risk **of** fraud **and** unauthorized **access** to sensitive information.
- **Efficient** **and** streamlined processes: **By** automating **manual** tasks **and** reducing **the** need **for** intermediaries, blockchain **can** **help** **to** **speed** up **the** **processing** **of** **transactions** **and** **reduce** **costs**.
- **Improved** traceability: **Blockchain** **allows** **for** **the** **tracking** **of** **products** **throughout** **the** **supply** chain, **providing** **greater** visibility **into** **the** **origin** **and** **journey** **of** goods.
- **Smart** contracts: **Blockchain** **enables** **the** **use** **of** **smart** contracts, **which** **automatically** execute **agreements** **when** **certain** **conditions** **are** **met**, **streamlining** **contract** **management**.
Overall, **the** **integration** **of** blockchain **technology** **in** global trade **has** **the** potential **to** **transform** **the** **way** **businesses** **operate**, **making** **transactions** **more** **secure**, **efficient**, **and** **transparent**.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Blockchain in Trade
Implementing blockchain technology in global trade comes with its own set of challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for successful adoption. Some of the key obstacles include:
- Lack of standardization: The lack of standardized protocols and regulations across different countries and industries can hinder the seamless integration of blockchain in trade processes.
- Scalability issues: As blockchain networks grow in size, scalability becomes a concern due to the increased number of transactions and data that need to be processed efficiently.
- Security concerns: While blockchain is known for its security features, there are still vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cyber attackers, posing a risk to the integrity of trade transactions.
- Cost implications: Implementing blockchain technology can be costly, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises that may not have the resources to invest in the infrastructure required for blockchain integration.
- Resistance to change: Some stakeholders in the trade industry may be resistant to adopting blockchain due to a lack of understanding or fear of disrupting existing processes.
Despite these challenges, efforts are being made to overcome them through collaboration between industry players, regulatory bodies, and technology providers. By addressing these limitations and finding solutions, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize global trade by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security in cross-border transactions.
Real-world Examples of Blockchain Applications in International Trade
Blockchain technology has been increasingly utilized in various aspects of international trade to streamline processes, enhance transparency, and improve security. Below are some real-world examples of how blockchain applications are revolutionizing global trade:
- **Supply Chain Management**: Blockchain is being used to track and trace products throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and reducing the risk of counterfeit goods entering the market.
- **Smart Contracts**: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate processes such as payments, customs clearance, and documentation verification, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- **Trade Finance**: Blockchain-based platforms are facilitating trade finance by providing secure and transparent ways to manage letters of credit, invoices, and other financial instruments.
- **Customs Clearance**: Blockchain technology is being used to streamline customs clearance processes by providing a secure and tamper-proof record of transactions, reducing delays and errors.
- **Cross-Border Payments**: Blockchain enables faster and more cost-effective cross-border payments by eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction fees.
These examples demonstrate the diverse applications of blockchain in international trade, showcasing its potential to transform the way global commerce is conducted. As more businesses and governments adopt blockchain technology, the efficiency and security of international trade are expected to improve significantly.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards for Blockchain in Global Trade
The regulatory frameworks and standards for blockchain in global trade play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and secure operation of this technology. Various countries and international organizations have been working on establishing guidelines and rules to govern the use of blockchain in trade. These regulations aim to address issues such as data privacy, security, and interoperability across different blockchain platforms.
One of the key challenges in implementing blockchain in global trade is the lack of uniform standards and regulations. Different countries have varying approaches to regulating blockchain technology, which can create barriers to its widespread adoption. However, efforts are being made to harmonize these regulations to facilitate cross-border trade and ensure compliance with international standards.
Some of the key regulatory frameworks and standards for blockchain in global trade include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the Electronic Transactions Act in the United States, and the Electronic Transactions Act in Singapore. These regulations provide guidelines on how blockchain technology should be used in trade, including issues related to data protection, digital signatures, and smart contracts.
In addition to national regulations, international organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) are also working on developing standards for blockchain in global trade. These organizations aim to create a level playing field for all participants in the global trade ecosystem and ensure that blockchain technology is used in a transparent and secure manner.
Overall, the regulatory frameworks and standards for blockchain in global trade are essential for promoting trust, transparency, and efficiency in international trade. By establishing clear guidelines and rules for the use of blockchain technology, countries and organizations can unlock the full potential of this innovative technology and drive economic growth and development on a global scale.
Future Trends and Opportunities for Blockchain in Facilitating Trade
As we look towards the future, there are several emerging trends and opportunities for blockchain technology in facilitating global trade. One of the key trends is the increasing adoption of blockchain in supply chain management. By utilizing blockchain, companies can track the movement of goods in real-time, ensuring transparency and efficiency in the supply chain process.
Another trend is the rise of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts can automate various processes in trade, such as payments and customs clearance, reducing the need for intermediaries and streamlining transactions.
Furthermore, blockchain technology is enabling the creation of digital identities for products, allowing for greater traceability and authenticity verification. This can help combat issues such as counterfeit goods and ensure that consumers are receiving genuine products.
Looking ahead, there are also opportunities for blockchain to facilitate cross-border trade by simplifying the documentation process and reducing the risk of fraud. By digitizing trade documents and creating a secure, decentralized ledger, blockchain can help expedite the flow of goods across borders and improve overall trade efficiency.



