The Role of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
- Understanding the Basics of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
- Exploring the Various Types of Consensus Mechanisms Used in Blockchain Technology
- The Importance of Consensus Mechanisms in Maintaining Security and Integrity in Blockchain Networks
- Comparing Proof of Work and Proof of Stake: Two Popular Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
- Challenges and Limitations of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Technology
- Future Trends and Innovations in Consensus Mechanisms for Blockchain Networks
Understanding the Basics of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
Blockchain technology relies on **consensus mechanisms** to ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions. These mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain by preventing fraudulent activities such as double-spending.
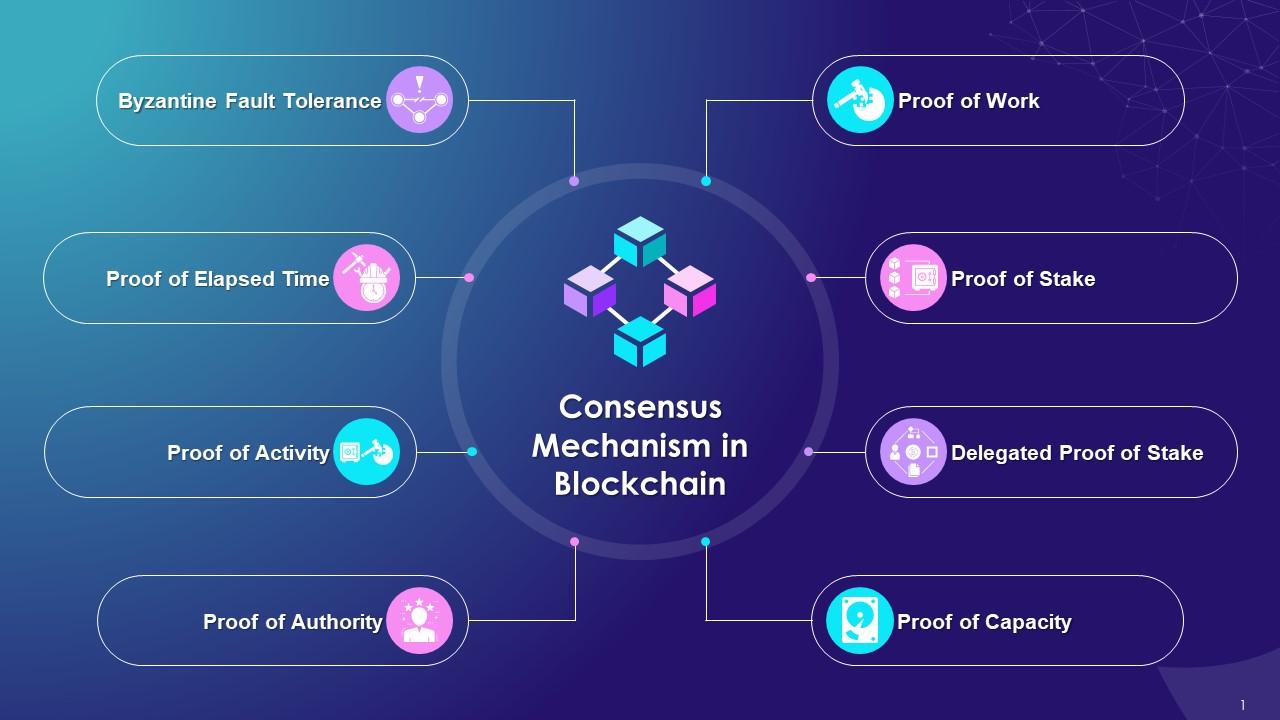
There are several types of **consensus mechanisms** used in blockchain networks, each with its unique way of reaching an agreement among network participants. Some of the most common **consensus mechanisms** include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
**Proof of Work** is the original **consensus mechanism** used in the Bitcoin blockchain, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. **Proof of Stake**, on the other hand, selects validators based on the number of coins they hold, incentivizing them to act in the best interest of the network.
**Delegated Proof of Stake** introduces a democratic element by allowing coin holders to vote for delegates who will validate transactions on their behalf. This **consensus mechanism** is known for its scalability and energy efficiency compared to PoW.
**Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance** is another **consensus mechanism** that focuses on reaching an agreement in a network where some participants may be malicious. By tolerating a certain number of faulty nodes, PBFT ensures that the network can continue to operate smoothly even in the presence of bad actors.
Understanding the basics of **consensus mechanisms** in blockchain is essential for anyone looking to grasp the inner workings of this revolutionary technology. By ensuring agreement among network participants, **consensus mechanisms** enable blockchain to function as a decentralized and secure system for recording transactions.
Exploring the Various Types of Consensus Mechanisms Used in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology relies on various types of consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and secure the network. These mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of the blockchain. Let’s explore some of the most commonly used consensus mechanisms in blockchain technology:
1. **Proof of Work (PoW):** PoW is the original consensus mechanism used in blockchain technology, most notably in Bitcoin. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process requires a significant amount of computational power, making it secure but energy-intensive.
2. **Proof of Stake (PoS):** In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This mechanism is more energy-efficient than PoW but still ensures network security. Ethereum is in the process of transitioning from PoW to PoS with its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
3. **Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS):** DPoS is a variation of PoS where coin holders vote for delegates to validate transactions on their behalf. These delegates take turns producing blocks, making the consensus process more efficient. EOS and TRON are examples of blockchains that use DPoS.
4. **Proof of Authority (PoA):** PoA relies on a set of approved validators who are known entities with established identities. These validators take turns creating new blocks, and their reputation is at stake, incentivizing them to act honestly. PoA is often used in private or consortium blockchains.
5. **Proof of Space (PoSpace):** PoSpace requires participants to allocate a certain amount of disk space to the network to validate transactions. This mechanism leverages unused storage space rather than computational power, making it more environmentally friendly.
6. **Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET):** PoET is a consensus mechanism designed to be fair and energy-efficient. Participants in the network wait for a randomly chosen amount of time before being eligible to create a new block. This randomness prevents any single entity from gaining an advantage.
By understanding the various types of consensus mechanisms used in blockchain technology, we can appreciate the diversity of approaches to achieving agreement in a decentralized network. Each mechanism has its strengths and weaknesses, catering to different priorities such as security, scalability, and energy efficiency. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, new consensus mechanisms may emerge, further enhancing the capabilities of this groundbreaking technology.
The Importance of Consensus Mechanisms in Maintaining Security and Integrity in Blockchain Networks
Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain networks. These mechanisms are essential for reaching an agreement among network participants on the validity of transactions and the state of the ledger. By establishing a consensus, blockchain networks can prevent fraud, double-spending, and other malicious activities.
One of the key benefits of using consensus mechanisms is that they help maintain the decentralized nature of blockchain networks. By requiring majority approval for transactions to be added to the ledger, consensus mechanisms ensure that no single entity can control the network. This decentralization is what makes blockchain technology so secure and resistant to censorship and tampering.
There are several types of consensus mechanisms used in blockchain networks, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). Each of these mechanisms has its unique way of reaching consensus and ensuring the security of the network.
Overall, consensus mechanisms are essential for maintaining the security and integrity of blockchain networks. Without a reliable consensus mechanism in place, blockchain networks would be vulnerable to attacks and manipulation. By requiring network participants to agree on the validity of transactions, consensus mechanisms help ensure that blockchain technology remains trustworthy and secure.
Comparing Proof of Work and Proof of Stake: Two Popular Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
When it comes to consensus mechanisms in blockchain technology, two of the most popular options are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain networks by enabling participants to agree on the validity of transactions.
Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism used in the Bitcoin blockchain. It requires participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process consumes a significant amount of computational power and electricity, making it resource-intensive.
On the other hand, Proof of Stake operates differently by allowing participants, known as validators, to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold. This means that the more coins a validator has, the more likely they are to be chosen to create a new block. PoS is considered to be more energy-efficient compared to PoW.
While both PoW and PoS have their strengths and weaknesses, the choice between the two consensus mechanisms ultimately depends on the specific needs and goals of a blockchain network. Some networks may prioritize security and decentralization, making PoW a better option, while others may value scalability and energy efficiency, favoring PoS.
Challenges and Limitations of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Technology
There are several challenges and limitations associated with consensus mechanisms in blockchain technology. One of the main issues is the high energy consumption required by some consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work. This energy-intensive process can be environmentally unsustainable and costly. Another challenge is the potential for centralization that can occur with certain consensus mechanisms, where a small number of participants may have a disproportionate amount of influence over the network.
Additionally, scalability is a common limitation of many consensus mechanisms. As blockchain networks grow in size and complexity, the consensus algorithm may struggle to keep up with the increasing number of transactions, leading to slower processing times and higher fees. Security is also a concern, as some consensus mechanisms may be vulnerable to attacks such as 51% attacks, where a single entity gains control of the majority of the network’s computing power.
Furthermore, the governance of blockchain networks can be a challenge when it comes to building consensus among participants with different interests and incentives. This can lead to disagreements and forks in the network, potentially causing disruptions and fragmentation. Overall, while consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and security of blockchain networks, it is important to be aware of the challenges and limitations associated with them in order to address them effectively.
Future Trends and Innovations in Consensus Mechanisms for Blockchain Networks
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, there are several future trends and innovations in consensus mechanisms that are shaping the landscape of blockchain networks. These advancements are crucial in ensuring the security, scalability, and efficiency of blockchain systems.
One of the emerging trends in consensus mechanisms is the move towards more energy-efficient protocols. Traditional proof-of-work algorithms, such as those used by Bitcoin, require significant computational power and energy consumption. In response to these concerns, new consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake and delegated proof-of-stake are gaining popularity for their lower energy requirements.
Another trend in consensus mechanisms is the focus on scalability. As blockchain networks grow in size and complexity, the need for faster transaction processing becomes more pressing. Innovations like sharding, sidechains, and off-chain scaling solutions are being developed to address these scalability challenges and improve the overall performance of blockchain networks.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in hybrid consensus mechanisms that combine the strengths of different protocols to achieve a balance between security, decentralization, and efficiency. By leveraging the unique features of multiple consensus algorithms, these hybrid mechanisms aim to provide a more robust and flexible foundation for blockchain networks.
In conclusion, the future of consensus mechanisms in blockchain networks is marked by a shift towards energy-efficient, scalable, and hybrid protocols. These innovations are essential for overcoming the limitations of existing consensus algorithms and unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology in various industries.



